
by revityteam | Aug 30, 2023 | TMS Therapy
If you’ve been dealing with anxiety and are exploring different treatment options, you’ve come to the right place. In this blog, we will dive deep into the world of TMS therapy for anxiety.
You might be wondering, what exactly is TMS for anxiety? How does it work? Is it effective?
Well, worry not because I’ll guide you through everything you need to know about TMS for anxiety. So, grab a cozy seat, sip on your favorite beverage, and let’s embark on this journey together to explore this innovative and potentially life-changing therapy. Are you ready? Let’s get started!
The Science Behind TMS
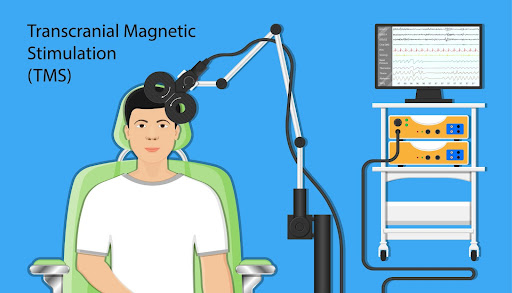
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation is a cool technique that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific regions of the brain. An electromagnetic coil is placed near the skull, generating magnetic fields to stimulate the underlying brain cells. We use TMS to target specific areas of the brain that are believed to be involved in mood regulation, like the prefrontal cortex.
While we don’t know exactly how TMS treats anxiety, it is believed to have a modulating effect on the neural circuitry involved in anxiety disorders. By delivering magnetic pulses to the brain, TMS can alter the activity of the targeted brain regions, which helps regulate emotional processing and reduce anxiety symptoms.
The big advantage of TMS over traditional treatments like medication or therapy is that it is non-invasive. It can provide a localized stimulation to the brain regions specifically implicated in anxiety disorders, resulting in a more precise and focused effect in relieving anxiety symptoms. Since it’s non-invasive, it’s a safer and more accessible treatment option for many people.
Overall, the science behind TMS suggests a promising technique worth looking into if you or anyone else you know is struggling with anxiety.
Common Types of Anxiety Disorders Treated With TMS

1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
GAD is an anxiety disorder where a person experiences excessive, uncontrollable worries and fears about various aspects of their life. It’s like having that “what if” feeling on steroids, where the worries and fears persist even when there’s no real threat or reason to be worried.
People with GAD often find it difficult to control their worry, which can interfere with their day-to-day activities and quality of life. They might feel restless, irritable, and have difficulty concentrating. Physical symptoms like muscle tension, headaches, and fatigue are also common.
You might be wondering what causes GAD. Well, it’s a combination of factors like genetic predisposition, brain chemistry, and environmental factors. Stressful life events, such as trauma or major life changes, can also contribute to the development of GAD.
The good news is that GAD is treatable! Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), is often the go-to treatment. It helps individuals identify and challenge their anxious thoughts and develop coping strategies. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms.
2. Panic Disorder:
Picture this – you suddenly feel an overwhelming sense of fear or apprehension that seems to come out of nowhere. Your heart starts racing, you have trouble breathing, and you feel like you’re going to lose control or even die. This intense episode is known as a panic attack. Now, imagine experiencing these panic attacks on a recurring basis, with a constant fear of having more. That’s what it’s like for someone with panic disorder. They often live in fear of when the next attack will strike, and this fear can start to impact their daily life.
People with panic disorder may avoid certain situations or places because they fear it will trigger another panic attack. They may worry excessively about having a panic attack in public or being unable to get help if needed. The fear of panic attacks can become so intense that it restricts their activities and affects their overall well-being. While the exact cause of panic disorder is not fully understood, it’s believed to be a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors. Sometimes, panic disorder can develop after a major life stressor or traumatic event, but it can also occur without any identifiable trigger.
The good news is that there are effective treatments for panic disorder. Therapy, particularly CBT, can help individuals understand the underlying thoughts and behaviors contributing to their panic attacks. Medications may also be prescribed to manage the symptoms and provide relief. Remember, panic disorder is a real and treatable condition. People can learn to manage their symptoms and regain control of their lives with the right support and resources.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder:
SAD is an anxiety disorder where a person experiences intense fear or discomfort in social situations or situations where others may evaluate them. This fear can feel quite overwhelming and can interfere with their daily life.People with SAD often worry about being judged or criticized negatively by others, which can lead to avoiding social situations altogether.
For example, they may avoid public speaking or participating in group activities because they’re afraid they’ll embarrass themselves or say something wrong.As you can imagine, this fear and avoidance can become isolating and affect someone’s self-esteem and confidence. Sometimes, it can impact their ability to work or maintain relationships.
The cause of SAD is not fully understood, but it’s believed to be a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors. It often develops during adolescence or early adulthood but can occur at any age
The good news is that there are effective treatments for SAD! Once again, CBT is often the go-to treatment. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to manage the symptoms.The most important thing to remember is that SAD is a real condition, and there should be no shame in seeking help for it.
4. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder:
Imagine having persistent, intrusive thoughts or fears that keep popping up in your mind. These thoughts are called obsessions, and they can be pretty distressing.For example, you may think you left the door unlocked or might harm someone unintentionally. These thoughts create a sense of anxiety and discomfort. And here’s the tricky part – to try and alleviate these obsessions, you may find yourself engaging in certain behaviors or rituals. These behaviors are called compulsions.
Compulsions are repetitive actions or mental acts you feel driven to perform to reduce your anxiety from the obsessions. For instance, you may feel compelled to wash your hands excessively, count things a specific number of times, or arrange objects in a particular order.
Performing these rituals or behaviors may provide temporary relief, but it’s only temporary. The obsessions and fears tend to come back, leading to a cycle of obsessions and compulsions that can be challenging to break.
Now, let’s talk about the causes of OCD. It’s complex and can involve a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors. Sometimes, stress or certain life events can trigger the onset or exacerbation of OCD symptoms.
The good news is that there are effective treatments for OCD. Therapy is often used to help individuals understand their obsessions, challenge their beliefs, and develop healthier coping strategies. In some cases, medication can also be prescribed to help manage the symptoms.
Remember, you don’t have to face OCD alone. With the right support and treatment, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
5. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder:
PTSD can develop after someone has experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. It can affect individuals of any age, gender, or ethnicity, making it challenging to reintegrate into daily life.
Now, let me give you an idea of what PTSD can feel like. Imagine experiencing consistent and intense feelings of anxiety, fear, depression, and avoidance following a traumatic experience like an accident, violent assault, or natural disaster. These symptoms can persist for weeks or months and might even last for years if not treated.
Common symptoms of PTSD include intrusive thoughts or memories about the traumatic event, nightmares or flashbacks, feeling numb or detached, avoiding places or people that remind you of the trauma, or feeling edgy or easily startled. All of these symptoms can have a profound impact on someone’s daily life, work, and relationships.
So, what causes PTSD? Traumatic experiences are a significant factor, but additional factors such as prior trauma, genetics, or poor coping strategies can also contribute to the development of PTSD.
The good news is that there are effective treatments for PTSD. Therapy can work to desensitize the individual to the trauma, alter how they perceive their experience, and develop coping strategies. In some instances, medication may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
Remember, with the right treatment and support, people with PTSD can move towards healing and find relief.

TMS Effectiveness and Research
To date, several small studies have shown that TMS may be effective in treating anxiety disorders such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, social anxiety disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder. In some of these studies, patients experienced a significant reduction in their symptoms of anxiety.
While the evidence is promising, it’s important to note that TMS for anxiety is not yet considered a first-line treatment; it’s typically reserved for patients who have not responded to other forms of treatment. For instance, antidepressant medication and psychotherapy are the standard first-line treatments for anxiety.
When comparing TMS to more traditional forms of treatment for anxiety, it’s worth noting that TMS is a newer and less-researched treatment modality. Antidepressant medication and psychotherapy have years of research behind them and are considered effective, safe, and well-established treatments for anxiety disorders.
However, traditional treatments are not always effective for every patient, and some individuals may not be able to tolerate the side effects of medication. In those cases, TMS may offer a useful alternative or adjunct treatment that is non-invasive and has fewer side effects.
TMS Treatment Process
The TMS treatment process typically consists of several steps, from an initial evaluation to multiple TMS sessions. Let me walk you through what to expect before, during, and after TMS treatment.
Before TMS Treatment:
Before starting TMS, you will undergo an initial evaluation with a trained provider who will assess your suitability and determine your treatment plan. During this initial assessment, it’s important to disclose current medications, medical history, and other factors that could interfere with TMS therapy.
For example, TMS therapy isn’t usually a good idea if you have a metal device like a cochlear implant or have a history of seizures.
During TMS Treatment:
During a TMS treatment session, the patient will be seated in a comfortable chair and wear earplugs to protect against the noise of the TMS machine. The TMS practitioner will then place a small magnetic coil over your head and begin stimulating a specific area of your brain with rapidly oscillating magnetic pulses.
Each pulse is about the duration of a sound “click.” The stimulation will feel like a tapping sensation on your scalp, but it generally doesn’t hurt. You can resume your regular activities after the TMS session.
After TMS Treatment:
After the TMS session, you should be able to return to your daily routine without interference. You can drive, work, and do other regular activities without limitations or downtime.

Role of a TMS Provider
The role of a TMS provider is to administer TMS therapy to patients with appropriate indications. TMS providers are typically trained professionals with knowledge and expertise in delivering TMS treatment.
TMS providers are responsible for assessing the suitability of patients for TMS therapy, determining the treatment parameters (such as the location and intensity of stimulation), and delivering the treatment sessions. They closely monitor the patient’s progress throughout the treatment and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
In addition to administering TMS, TMS providers may also play a role in scheduling appointments, providing education and support to patients before and during treatment, and coordinating with other treatment team members to ensure the patient receives comprehensive care.
It’s important to note that the role of a TMS provider may vary depending on the specific clinical setting and the multidisciplinary team involved in delivering TMS therapy. Therefore, a TMS provider’s responsibilities and scope of practice may differ to some extent.
Finding and Choosing a TMS Provider
When it comes to finding and choosing a TMS provider, here are some tips that may help you:
1. Finding Providers:
Start by asking your primary care doctor or mental health professional for recommendations. They may be able to provide you with a list of TMS providers in your area.
You can also use online directories or search engines to find TMS providers near you. Look for reputable medical centers, hospitals, or clinics offering TMS therapy as treatment options.
2. Factors for Choosing a Provider:
When choosing a TMS provider, there are several important factors to consider:
- Experience and Credentials: Look for a provider with experience and expertise in TMS therapy. Check their credentials and ensure they are trained and certified in delivering TMS treatment.
- Reputation and Reviews: Research the provider’s reputation by reading online reviews or testimonials from other patients. This can give you a sense of what to expect regarding care and treatment outcomes.
- Communication and Comfort: It’s essential to feel comfortable and communicate well with your TMS provider. They should take the time to listen to your concerns, answer your questions, and explain the treatment process to you clearly.
- Insurance and Cost: Check if the provider accepts your insurance and inquire about the cost of treatment. Find out if they offer financial assistance or payment options to make it more affordable.
- Location and Convenience: Consider the location and convenience of the provider’s office. It can be helpful to choose a provider close to your home or work to make it easier to attend regular treatment sessions.
3. Questions to Ask During the Consultation:
Don’t hesitate to ask questions when you consult a potential TMS provider. Here are some important ones to consider:
- How much experience do you have with TMS treatment?
- What success rates have you seen with TMS for my specific condition?
- What side effects should I expect from TMS?
- How long is each treatment session, and how many will I need?\
- Will I need any additional treatments alongside TMS therapy?
- Do you accept my insurance, and what will the cost of treatment be?
- Can you provide any references or testimonials from previous patients?
Remember, my friend, it’s important to take the time to find a reputable and qualified TMS provider who makes you feel comfortable and confident in the treatment they offer. Don’t hesitate to consult multiple providers to find the best fit for you!
TMS Therapy With Brain Health Center
If you’re feeling inspired by the potential of TMS therapy for anxiety, I encourage you to take the next step toward finding relief. Contact Brain Health Center to explore our TMS treatment options. Our experienced, compassionate team is dedicated to providing high-quality care and helping individuals like you on your journey to mental wellness.
Don’t hesitate to reach out and inquire about TMS therapy for anxiety. Remember, you don’t have to face anxiety alone – support and effective treatments are available. Reach out to Brain Health Center today, and let us guide you on your path to healing.

by revityteam | Aug 23, 2023 | TMS Therapy
TMS therapy for children is a promising approach for treating neuropsychiatric conditions in kids. Neuropsychiatric conditions are disorders that affect both neurology and psychiatry.
TMS therapy uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain and help ease symptoms of disorders like ADHD, depression, and OCD in children. You must be wondering, how effective is it?
Well, let’s dive into the research and explore the effectiveness of TMS therapy in treating these conditions in children. By understanding the potential benefits and things to consider, we can make informed decisions to support children’s mental health and well-being. Let’s go!
Understanding How TMS Therapy Works
Of course, before we delve into the specifics of TMS therapy for children, it’s important to review TMS therapy in general.
TMS therapy, also known as Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, is an interesting treatment option for mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and ADHD. It’s a non-invasive procedure that uses a special device with an electromagnetic coil.
During a TMS therapy session, they place a coil on the scalp, sending out short magnetic pulses. These pulses go through the skull and into specific parts of the brain. It’s pretty cool how they can target deeper areas of your brain, up to a couple of centimeters beneath the scalp!
The idea behind TMS therapy is to stimulate the areas of the brain responsible for regulating mood and emotions, especially the prefrontal cortex.
Increasing the activity of the nerve cells in that region and balancing neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine can help improve mood and alleviate symptoms of mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, OCD, ADHD, and autism spectrum disorder.
The best part is that the treatment is painless and requires no anesthesia or medications. For example, those undergoing TMS therapy don’t have to stay in the hospital. Sessions take around 20-40 minutes, a few times a week, for about a month or so.
That is unless we’re talking about advanced TMS. Those sessions only last for one week but involve multiple treatment sessions per day. The type of TMS treatment you choose is an individualized process you can discuss with your provider.
During the sessions, the patient is fully awake and can even do things like read a book or watch TV. It’s pretty convenient, right? And the cool thing about TMS therapy is that it has shown promising results, especially for people who haven’t found relief with other treatments or can’t tolerate medications. There is hope for relief.
So, if you’re struggling with depression or another mental health condition and you’re looking for a different approach, TMS therapy could be worth considering. It’s something worth discussing with your doctor to see if it might be a good fit for you.
TMS Therapy Application in Children
Now let’s discuss TMS therapy for children. For the most part, you’ll see TMS therapy advertised for adults ages 18 and over. This is because of the electromagnetic coil used in TMS treatment.
Many providers use a helmet instead of a coil, and that helmet only works on adults. But providers who use a coil can treat younger patients as long as they can collect the necessary data for proper treatment.
As it turns out, some children are good candidates for TMS therapy. It all depends on their age and whether the electromagnetic coil fits. Generally speaking, children younger than 11 aren’t ready for TMS therapy because their heads are too small, and the provider can’t collect the needed data.
If you aren’t sure whether a child’s head is big enough, you can take them to a TMS treatment center to see.
TMS for children is very effective when it’s used. There are a number of small trials and literature reviews that are a testament to that, but most of them are behind databases and journals with paywalls, making them difficult for most people to access. So let us dish out all the details, so you’ll know what you’re dealing with.
Placebo Trials
Did you know there are placebo trials for TMS for children, just like there are for many different health conditions and proposed treatments? However, most parents won’t pick that for their children because they want results.
They don’t want to risk receiving the placebo and not getting results, nor do they want their child to feel like an experiment. Most of all, they just want their child to feel better. A placebo trial doesn’t always equate to the fastest treatment or feeling better immediately, so this is understandable.
Treatment Risks
Some parents worry about the risks associated with TMS for children. However, this isn’t a big concern because a seizure is the only real adverse reaction. The chances of a seizure are very low — the risk is about the same as having a spontaneous seizure from an antidepressant you’re taking — it’s very, very low.
Having said that, we should note that, with both TMS therapy and antidepressant medications, the chances of a child having a seizure are slightly higher than in adults.
Simply put, TMS for children is a highly effective treatment with few side effects, making it an excellent option for children old enough for the electromagnetic coil to fit their heads so that data can be collected. The key is finding a provider with the right equipment that can fit on smaller heads.
Conditions Treated With TMS for Children
Many children — specifically adolescents — suffer from conditions like depression, anxiety, ADHD, OCD, or autism spectrum disorder, but they can’t express it the same way adults can. While older teens and adults can describe how they feel, children don’t have the vocabulary. That, or they don’t recognize what they are feeling.
Let’s look at each of these conditions and what they look like in children.

Anxiety
When it comes to anxiety in children, it’s important to know that it’s actually quite common. Just like adults, kids can also experience anxiety, which can show up differently.
Imagine a child who’s dealing with anxiety. They may often feel extremely worried or fearful about everyday things. It could be related to school, making friends, or even going to a new place. Sometimes, these worries can be so intense that they interfere with their daily activities or social interactions.
Physically, anxiety in children can cause things like vomiting, restlessness, trouble sleeping, or even complaints of stomachaches or headaches. They may have difficulty concentrating or constantly seek reassurance from parents or caregivers.
Sometimes, they might avoid situations that trigger their anxiety, like attending school or participating in activities with their peers.
It’s important to realize that anxiety can vary from child to child. Some may have specific fears or phobias, like being scared of dogs or the dark.
Others might have generalized anxiety, where they worry about many things without a clear reason. And in some cases, anxiety can be linked to other conditions, such as ADHD or autism.
As a friend, it’s essential to be supportive and understanding. Anxiety can impact a child’s well-being and self-esteem. Encouraging open communication and providing a safe and calm environment can make a big difference.
Remember, anxiety in children is treatable, and with the right support, they can learn to manage their fears and worries. Be patient, be there for them, and let them know you’re in their corner. They’ll appreciate it more than you know!
Depression
Depression in children is a mood disorder characterized by persistent sadness, irritability, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed.
Children with depression may experience changes in sleep patterns and appetite and may exhibit withdrawal from social interactions.
They may also display signs of anger or irritability and have difficulty concentrating. In severe cases, depression in children can lead to thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
It is important to note that the symptoms of depression in children can vary and may not always be as apparent as they are in adults. Children may have difficulty understanding and expressing their feelings, making it challenging to recognize depression.
Many children with depression won’t say, “I have depression.” Instead, they might say, “I feel down” or “I feel sad.” So, again, if you’re hearing that or seeing that in a child, you’re likely witnessing depression.
An example of this would be a child who feels sick before going to school. They might throw up or have an upset stomach. But when summer comes, they are fine in the mornings. They have no sick symptoms. That’s because they no longer face the situation that was giving them anxiety.
So, if you think you’re noticing anxiety but aren’t sure, it’s a good idea to remove the child from the situation and see if that improves how they’re feeling.
If parents or caregivers notice any persistent changes in mood or behavior in their child, such as prolonged sadness, low energy, or changes in social interactions, it is important to seek professional help.
Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is characterized by difficulty staying focused, controlling impulsive behaviors, and regulating hyperactivity.
Controlling impulsive behaviors can take the form of speech, movement, action, or decision-making. Children with ADHD might talk more than normal, ask too many questions, or have trouble waiting for their turn to speak, resulting in lots of interruptions.
It can also really challenge them to filter their thoughts and regulate their speech.
Children with ADHD often show signs of inattention, forgetfulness, losing things, and having trouble completing tasks. They may also have difficulty with organization and time management, often resulting in missed deadlines and difficulty holding responsibilities.
On the other hand, hyperactivity and impulsivity may cause children with ADHD to fidget, squirm, or have trouble staying seated at school or during other activities.
It’s important to remember that while ADHD may present some challenges, children with ADHD can benefit from early diagnosis, medication, behavioral therapies, and other supportive strategies like TMS therapy.
With the right guidance and support, children with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and thrive in school and social settings.

Autism Spectrum Disorder
Let’s discuss autism spectrum disorder now. Commonly referred to as ASD, it’s a neurological condition that affects how a child interacts with others, communicates their needs, and perceives the world around them.
Children with ASD may have difficulty with social interactions, such as making eye contact or engaging in conversation, and may prefer to play alone or have repetitive behaviors.
Those repetitive behaviors include motor, verbal, ritualistic, and informational behaviors. Motor behavior includes hand flapping, rocking back and forth, or spinning around in circles. Verbal behaviors include repeating words or phrases repeatedly, even if they don’t seem to serve a communicative purpose.
Ritualistic behaviors often cause autistic children to be very rigid and structured in their routines. They might line up their toys in precise order or become upset if their routine is disrupted. Informational behaviors include intense interest or preoccupation with certain topics.
Some children with ASD may also have sensitivity to stimuli like light, sound, or touch, which can cause distress. Being exposed to specific light sources like bright sunlight or flickering overhead lights can make it difficult for them to concentrate or participate in activities.
Children with ASD often have a heightened sensitivity to certain sounds like sudden noises, high-pitched sounds, or even everyday background noises.
Some children may become distressed and cover their ears when they hear certain sounds. This can make it difficult for them to participate in social activities or interact in noisy environments such as classrooms, auditoriums, or playgrounds.
For some children with ASD, certain types of touch can be overwhelming or uncomfortable. They may become distressed at textures, tags on clothing, hair brushing, or certain types of fabrics.
ASD can be a spectrum disorder, meaning the severity of symptoms may vary in each child. Some children may have mild symptoms, while others may be more severely impacted.
It’s important to note that each child with ASD is unique and may experience different challenges. While some children with ASD may have difficulty with communication and sensory processing, others may excel in specific areas like music, mathematics, or art.
It’s essential to support children with ASD by encouraging their strengths and being patient with their challenges.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Finally, there’s obsessive-compulsive disorder. It’s essential to understand that OCD is a mental health condition characterized by obsessions and compulsions that can significantly impact a child’s daily life.
In OCD, children experience intrusive thoughts or images known as obsessions, which can lead to intense anxiety or distress. Obsessions can be about specific fears, such as germs, safety, or orderliness, and they can be persistent and difficult to control.
In an attempt to alleviate this anxiety, children with OCD develop repetitive behaviors or rituals, known as compulsions. These compulsions can involve excessive handwashing, repeatedly checking door locks, or arranging objects in a specific order.
OCD can become quite time-consuming, causing significant disruptions in a child’s daily routines, schoolwork, and relationships. It’s important to note that the severity of OCD symptoms can vary from mild to severe.
I want to emphasize that it’s crucial to approach OCD with understanding and support. Children with OCD often feel powerless and may be ashamed or embarrassed about their obsessions and compulsions. Providing them with reassurance and empathy is vital.
Now that we’ve covered what conditions TMS can be used to treat in children, let’s go back to discussing TMS, specifically the benefits for children, what they can expect during TMS therapy, and more.
Key Benefits of TMS for Children
One of the key benefits of TMS for children is that it’s non-invasive. Because no drugs are involved, the chances of a child becoming sick from TMS are next to none. The great part of TMS is how quickly it works, providing children with fast relief from their symptoms.
TMS for children differs from medication because they must remember to take the medication and deal with the side effects since medications aren’t as specific or targeted. Because TMS treatment is specific, targeted to specific brain areas, generalized side effects are eliminated.
What a Child Can Expect During TMS Therapy
Of course, children can have a harder time with discomfort, so it’s worth noting what to expect when they come to TMS therapy. Some children may handle TMS better than others, but it’s best to prepare for any situation.
Discomfort From the Coil
First, a child might experience discomfort where the coil sets and where it’s stimulating. This is because the coil’s stimulation causes a little muscle contraction and directly stimulates the nervous tissue below the skin. Once a child has completed five to 10 TMS treatments, it shouldn’t bother them anymore.
Keep in mind that it’s the head, not the brain, being stimulated, as our brains don’t have nerve endings. The nerve stimulation can cause your head to move and your eye to twitch. The eye-twitching part happens because the coil is set right above the periocular area.
These movements may be scary for a child to experience, so reassurance is imperative after treatment.
Mild Headache
Second, a child might experience a mild headache because so much of the head is being stimulated. The headaches usually last for the first five to 10 treatments. That could mean a day or two if the child receives accelerated TMS treatment or up to a week if they are doing traditional TMS.
As with most headaches, TMS-induced headaches can be treated with over-the-counter medications to provide relief. No one wants a headache that lasts for a long time!
To further aid your child with headaches, encourage them to rest and ensure they are drinking plenty of water.

Drowsiness
Third, drowsiness is a common symptom children experience when receiving TMS treatment. This drowsiness can hit during the TMS session and last for one to two hours afterward. Of course, an 11- to 14-year-old child won’t be driving yet, so getting home isn’t a concern. But it is something to be aware of.
How Long Does a TMS Session Last?
TMS for children lasts as long as it would for an adult with most of the same caveats.
How long the session lasts entirely depends on what the child is being treated for and where they’re receiving treatment.
At most advanced facilities, depression treatment takes about four minutes. However, it can last up to 36 minutes. It all depends on the patient and what they need. For anxiety, most sessions last 15 to 30 minutes. Anxiety treatments are a little bit gentler and generally tolerated well.
ADHD usually takes 10 to 20 minutes. For autism, specific symptoms are treated, so time frames vary.
The Strength of the Treatment
The major difference between adults and children receiving TMS isn’t in how long the session lasts but in how intense the treatment is. When a TMS session begins, single pulses are sent through the electromagnetic pulse.
How a child’s body reacts to that pulse determines the strength of the treatment. It’s usually much lower in children than it is for adults, making it much more tolerable for children.
Have More Questions? Contact Brain Health Center.
We’ve covered a lot in this blog, but that doesn’t mean you don’t have more questions! If you’re considering TMS therapy for your child, look no further than Brain Health Center.
We offer TMS for children using the electromagnetic coil discussed in this blog. Our providers are experts in administering TMS for children, so you can rest assured that they’re in good hands.
TMS for children is an innovative approach that can make a world of difference for a child suffering from a mental health condition or neurological disorder like autism. Let’s work together to make your child’s world a better place to be!
To start the process, call us at 435.900.0123, email us at hello@brainhc.com, fill out the form on our website, or visit us at our location in St. George, Utah.

by revityteam | Aug 16, 2023 | Depression
Depression is a common mental health condition that can come with debilitating side effects. It can affect anyone, no matter how old you are or what your background is. While prescription medications are often used when treating depression, there’s no guarantee you’ll respond well to them.
On the other hand, you might not be able to take depression medication if it negatively interacts with other medications you need.
Fortunately, there are many non-medication treatments and techniques that can help cure depression without medication. From psychotherapy to exercise and self-care, this article will explore the different ways you can treat depression without depression medication.
We will answer some commonly asked questions about non-medication depression treatment approaches and provide an overview of what you can realistically expect from these alternative options.
What Is Depression?
Depression is a mental health condition where a person feels ongoing sadness and hopelessness. It’s not just regular “feeling down” moments, either. It can interfere with a person’s daily life.
It’s pretty common, and there are different types of depression, like major depressive disorder, where you feel chronic depression that won’t let up, and postpartum depression, where you experience depression after having a baby. And that’s just scratching the surface.
While most people think of depression as something that goes in your head, that’s not always the case. Sometimes it can even affect you physically, messing with your energy levels, appetite, and sleep.
Medication Methods for Treating Depression
Depression medication isn’t always necessary. But when it is, it’s certainly a helpful tool for treating depression. We use antidepressants to alleviate symptoms. This works by regulating certain chemical levels in the brain. There are several classes of antidepressants, including SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, and MAOIs.
SSRIs, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, increase serotonin levels in the brain. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood. We consider SSRIs a first-line treatment for depression because of how effective they are and how few side effects they have.
SNRIs, or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, balance serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. They block the reabsorption of these two neurotransmitters, increasing their availability to transmit messages between brain cells.
TCAs, or tricyclic antidepressants, affect neurotransmitters involved in communication between brain cells. They are called tricyclic because of their unique three-ring molecular structure. Like most antidepressants, TCAs aim to change brain chemistry and the communication circuitry of brain nerve cells that regulate mood, ultimately easing depression.
MAOIs, or monoamine oxidase inhibitors, inhibit monoamine oxidase enzymes that generally break down dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the brain. There are non-selective and selective. Non-selective MAOIs work on both types of monamine oxidase enzymes, while selective MAOIs only work on one type of enzyme.
By blocking the breakdown of these neurotransmitters, MAOIs increase their availability in the brain to improve mood and alleviate depression symptoms.
The type of antidepressant prescribed to you will depend on your symptoms and how severe they are. Finding the right medication and dosage might take some time, and it’s important to understand that it could take several weeks to become fully effective.
You’ll want to attend regular checkups with your doctor to ensure the medication works well for you and that side effects are properly managed.
However, while medications are essential for some individuals with depression, anti-depressants aren’t for everyone, nor are they the only way to treat depression. It’s often a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and other treatments that prove to be most effective.
Together, these treatments can improve your mood, increase your feelings of well-being, and help you function better daily.

Non-Medication Methods for Treating Depression
Medication is only one piece of the puzzle. Several other methods have been proven effective in managing depression, including psychotherapy, lifestyle changes, a support network, stress reduction techniques, a healthy diet, routine and structure, and TMS therapy. But can you treat depression without medication? Let’s take a closer look.
- Psychotherapy is also called talk therapy. It’s a common, effective way to treat depression. It involves working with a therapist to explore your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors and develop healthy coping mechanisms. Different types of therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and psychodynamic therapy, can be tailored to your specific needs and goals.
- Making certain lifestyle changes can have a positive impact on your mood. Regular exercise, even a brisk walk or engaging in activities you enjoy, can boost endorphin levels and improve mood. Adequate sleep, regular sleep schedules, and good sleep hygiene can also help alleviate depressive symptoms.
- Building a strong support network is essential. Reach out to friends and loved ones who provide understanding and emotional support. Participating in support groups or engaging in online communities with people who share similar experiences can also be helpful.
- Stress can worsen depression symptoms, so finding healthy ways to manage stress is crucial. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation.
- While diet alone cannot treat depression, a balanced and nutritious diet can support overall mental and physical well-being. Focus on consuming various fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive processed foods, sugar, and caffeine, as they may negatively impact your mood.
- Establishing a daily routine can provide a sense of stability and purpose, which can be helpful in managing depression. Set realistic goals and prioritize activities that bring you joy and a sense of accomplishment.
- Trying TMS therapy, or transcranial magnetic stimulation, has promising results for treating depression. It works by delivering focused magnetic pulses to specific regions of the brain that are associated with mood regulation. TMS therapy aims to restore the brain’s natural balance and alleviate depression symptoms. It is often used for individuals who haven’t had success with other depression treatments.
Remember, everyone’s experience with depression is unique, so it’s important to find what works best for you. Finding the right combination of non-medication methods that effectively manage your symptoms may take time and experimentation.

Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
Are non-medication methods effective for all patients?
We know that psychotherapy, exercise therapy, and mindfulness-based interventions can truly help some people with depression. Having said that, they don’t help everyone, and how effective they are depends on how severe the depression is, how well you follow treatment, and what you personally prefer.
When should I choose non-medication vs. medication treatment?
This is a great conversation to have with your doctor. The decision depends on several factors and how bad your depression is. Medication is often the best option if your depression is debilitating and interfering with your ability to live life. If your depression is manageable, you might prefer a psychotherapy technique like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), physical therapy, or even nutritional counseling.
You should talk to your doctor about this because depression treatment is so individualized. Your preferences, medical history, allergies, intolerances, etc., all matter, and the decision to choose medication or non-medication treatment should be made as part of an overall treatment plan.
Is medication-free treatment permanent?
That depends on what type of treatment you’re receiving and how your depression reacts to it. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer here. Non-medication treatments can indeed lead to long-lasting improvements or remission of symptoms.
For example, physical therapy, CBT, acupuncture, or TMS therapy may help you achieve long-term relief. So could lifestyle changes.
However, I want you to remember that treatment varies for everyone. Medication-free treatment does not last for some people; medication is necessary for lasting change. The only way to find out is by working with your healthcare professional.
Can medication-free treatments be used with medication treatments?
Absolutely! It’s often a combination of both treatments where you see the best results. It’s referred to as combination therapy.
Combining medication and non-medication treatments can be particularly beneficial for depression and anxiety. Studies have shown that combining CBT with antidepressants can be more effective than either treatment alone. These combination approaches help to reduce symptoms, improve response rates, and prevent relapse.
If you want to try combination therapy, talk to your healthcare provider! They can provide you with the right resources to get started.
Are there circumstances where only medication treatment is the best option?
In some circumstances, yes. Medications can play a crucial role in managing mental disorders and conditions. They are often used in combination with psychotherapy or TMS therapy.
Medications for mental health can help alleviate your symptoms, stabilize your mood, and improve overall functioning. Medication may sometimes be necessary, especially in severe or acute depression.
I want you to understand that medication-only treatment depends on your individual circumstances and should be determined between you and your doctor. You should be involved in the decision-making process because it’s your health. Your doctor should be involved because of their extensive medical knowledge. Together, you can come up with an individualized treatment plan.

What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of medication-based treatments for my depression?
Medication-based treatments for depression can offer several potential benefits, but they also have potential disadvantages.
Benefits of medication-based treatments for depression include:
- Antidepressant medications can help alleviate symptoms such as persistent sadness, loss of interest, and feelings of hopelessness.
- Some individuals experience an improvement in mood, allowing them to engage more fully in daily activities and enjoy life.
- Medications can boost motivation, making it easier to enact lifestyle changes and engage in therapy or other forms of treatment.
- Many individuals with depression experience disruptions in sleep, and certain antidepressants can help regulate sleep patterns.
Despite these benefits, there are also potential drawbacks to consider:
- Antidepressant medications can cause a range of side effects, including nausea, weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and sleep disturbances.
- Delayed onset of effect: It may take several weeks for the full effects of the medication to be felt.
- Finding the most effective medication and dosage may involve a trial-and-error process, as different medications work differently for each individual.
- Stopping certain antidepressants abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, underscoring the importance of gradual tapering under medical supervision.
I want to remind you of how important it is to use medication-based treatments with your doctor guiding you. They can help you weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks. Medication might not be appropriate for everyone, and alternative non-medication treatments can be wonderfully effective.
Will TMS therapy interfere with medication?
TMS therapy is often used in conjunction with antidepressant medication. It is an outpatient procedure that does not require anesthesia or sedation, so it won’t interfere with when you can take medication. It is also generally safe and well-tolerated, with only mild side effects like headaches, dizziness, and light-headedness.
Ultimately, a decision to use medication with transcranial magnetic stimulation is essential. I highly recommend consulting with your doctor.
TMS Therapy With Brain Health Center
Are you tired of battling depression? Feeling like your treatment options have run dry? It’s time to turn to an innovative solution that can bring hope and relief to your life. Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy at Brain Health Center offers a powerful alternative for managing depression.
Whether you are already on medication or prefer to explore non-medication options, TMS therapy can be an effective choice. It can be used as a standalone treatment or in conjunction with medication to enhance its effectiveness and provide lasting relief from depression.
Don’t let depression hold you back any longer. It’s time to take control of your mental health and revitalize your life with TMS therapy at Brain Health Center. Reach out to us now to schedule a consultation and learn more about how TMS therapy can provide the breakthrough you’ve been seeking.
Remember, brighter days are within reach. Let us help you rediscover joy and embrace a future filled with hope. Act now, and embark on your journey towards better mental health.
Call Brain Health Center at 435.900.0123, email us at hello@brainhc.com, and visit our website to schedule your TMS therapy today.

by revityteam | Aug 9, 2023 | TMS Therapy
There are many questions on the internet about how transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) therapy works. Whether you’re interested in TMS therapy for depression, anxiety, OCD, ADHD, autism, or other conditions, this blog answers people’s most common questions.
All Your Questions Answered:
1. How does TMS therapy work?
TMS therapy is a treatment method that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain involved in controlling our mood. During a session, they place an electromagnetic coil against the scalp during a session, usually near the forehead. This coil sends out repetitive magnetic pulses that stimulate the nerve cells in the brain. By doing this, TMS therapy can help regulate mood by increasing and regulating activity throughout the brain. Pretty cool, right? The best part is that TMS therapy is non-invasive and painless. You don’t need anesthesia or sedation, making it a much easier experience than other treatments.
2. What conditions can TMS therapy treat?
TMS therapy can treat several conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), bipolar disorder, and chronic pain. TMS therapy has also been used to treat other conditions like schizophrenia, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
3. Is TMS therapy safe?
TMS therapy is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, with common side effects being minor and easily managed.
4. What are the side effects of TMS therapy?
Like any medical procedure, it may have some side effects. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, including headaches, dizziness, and light-headedness. I have heard of rare cases where seizures have been reported. We recommend contacting a qualified TMS provider if you are considering TMS therapy and have any questions or concerns.
5. How long does TMS therapy take?
So, TMS therapy usually involves several weeks of treatment, but this advanced version only takes one week with multiple sessions per day. The duration and frequency of TMS sessions can vary depending on what your doctor recommends and what you need specifically.
Usually, a TMS therapy session lasts between 30 and 60 minutes. They’ll place a magnetic coil on your scalp and use it to deliver quick magnetic pulses to stimulate specific areas of your brain. It’s painless and non-invasive, so no need to worry!
Unless you are doing advanced TMS therapy, the typical treatment schedule is five days a week, from Monday to Friday, and it goes on for about 4 to 6 weeks.
To figure out the exact duration and frequency that suits you, it’s important to chat with a TMS specialist. They’ll work with you to create a personalized treatment plan based on your goals and needs.
6. How many TMS therapy sessions are needed?
The number of TMS therapy sessions required can vary depending on the specific treatment plan recommended for you.
It’s important to remember that everyone’s experience with TMS therapy will vary, so your number of sessions might differ from someone else’s. But when you work with your TMS specialist, they’ll create a personalized treatment plan designed uniquely for you.
7. Does insurance cover TMS therapy?
The answer depends on your insurance plan and personal situation. Some insurance companies cover TMS therapy since it’s considered medically necessary for treating depression. However, coverage is only sometimes guaranteed, and there may be specific criteria you need to meet for TMS therapy to be covered.
To find out if your insurance plan covers TMS therapy, your best bet is to contact your insurance provider and ask them for more information. They can give you specific details about the coverage options available to you.
8. Will I need maintenance TMS therapy sessions after my initial treatment?
Maintenance TMS therapy can be beneficial for preventing relapse in patients with treatment-resistant depression.
While many TMS patients experience relief from depression after the initial treatment and may not require further TMS or other forms of treatment, it doesn’t guarantee a completely depression-free life for everyone.
The need for maintenance TMS therapy can vary depending on individual circumstances and the severity of the condition. It is recommended to consult with your TMS specialist to determine whether maintenance sessions would be beneficial for you.

9. How does TMS compare to medication for treating depression?
TMS may be more effective than medication for patients who have not responded to multiple antidepressant medications. TMS has fewer side effects than medication, which is significant since side effects with medications can lead to discontinuation of treatment.
Having said that, everyone is different. For some people, TMS works great as a companion to an antidepressant. Ultimately, discussing TMS with your healthcare provider and TMS specialist is best to determine what will work for you.
10.Can TMS therapy be used in combination with medication?
Absolutely! For many individuals, TMS therapy and an antidepressant are the perfect combination to treat depression, anxiety, or other conditions.
11. How long do the effects of TMS therapy last?
This also varies by person. Some patients experience weeks or even months of symptom relief after completing a course of TMS therapy. In contrast, others may require additional treatment or follow-up sessions to sustain the therapeutic benefits.
12. How do I prepare for a TMS therapy session?
First, wearing comfortable clothing without any metals, jewelry, or accessories is important, as these could interfere with the TMS equipment. TMS therapists typically provide earplugs to reduce the noise level from the machine, but you may choose to bring your own headphones if you prefer.
Before the session, you’ll also want to avoid consuming beverages with caffeine or alcohol, as they can affect the brain’s activity and potentially impact the TMS session. You may also be instructed to avoid certain medications, such as anti-anxiety and muscle relaxant drugs.
During the session, you’ll be seated in a comfortable chair, and the TMS device will be positioned on your scalp, emitting a series of magnetic impulses. The sensation varies from person to person, but it’s generally described as a tapping or knocking feeling on the treatment area.
13. What should I expect after a TMS therapy session?
Unlike some other treatments, no sedation or anesthesia is administered during TMS therapy, so you should be fine after TMS therapy. You can drive yourself home and resume normal activities.
Regarding immediate effects, some people may experience mild side effects such as scalp discomfort or headache, but these are generally mild and temporary. These effects usually diminish shortly after the session ends and decrease over time with subsequent sessions.
14. Are there any restrictions on activities after a TMS therapy session?
You do not need to follow any restrictions after a TMS therapy session.
15. How do I know if TMS therapy is working for me?
Figuring out if TMS therapy is working for you can be a bit of a process, but here are some things to look out for:
- Pay attention to your symptoms: If you start to notice a decrease in the severity and frequency of your depression, anxiety, or whatever condition you’re targeting, that’s a good sign that TMS therapy is working. You might feel a sense of relief, improved mood, or just an overall better state of mind.
- Check your quality of life: TMS therapy aims to make your life better as a whole. If you find yourself performing daily activities more easily, enjoying hobbies more, and having better interactions with others, it may be a clue that the treatment is working.
- Ask for feedback: Sometimes, noticing changes in ourselves is hard. That’s when talking to trusted family, and friends can be helpful. They might see positive changes in your behavior, mood, or how you’re doing overall. Their observations can give you more insight into whether TMS therapy is making a difference.
- Keep talking with your doctor: Your healthcare provider will regularly check in with you to see how you’re doing during TMS therapy. It’s super important to keep them updated on your progress, symptoms, and anything else you notice. They’ll use this information to make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan so you get the best results possible.
Everyone’s response to TMS therapy might differ, so it’s important to be patient and stay in touch with your doctor to track your progress effectively.
TMS Therapy With Brain Health Center in St. George, Utah
Whether you’re looking into TMS therapy for yourself or someone you love, it’s an excellent treatment option for depression, anxiety, autism, ADHD, OCD, and more.
For more information on TMS therapy, contact Brain Health Center today. We’re here to provide high-quality treatment to help alleviate your symptoms and improve your quality of life.

by revityteam | Jul 19, 2023 | TMS
Suicidal thoughts and suicidal ideation are, unfortunately, becoming common in our world today. But thankfully, it’s not something any of us have to go through alone with the resources available to us. Today’s blog is all about suicidal ideation – what it is, how to treat it, and more. We hope this blog sheds light and hope, no matter who you’re reading it for.
What Is Suicidal Ideation?
Imagine feeling overwhelmed and burdened by thoughts of ending your own life. This is what suicidal ideation is – when a person experiences persistent and intrusive thoughts about self-harm or suicide. It’s important to understand that suicidal ideation is not a choice or a reflection of weakness. Instead, it’s a sign of the immense pain and despair that someone may be going through.
Now, I want you to understand that suicidal ideation can manifest in different forms, ranging from fleeting thoughts to detailed plans. These thoughts can be distressing and consuming, making it difficult to find relief. It’s crucial to remember that experiencing suicidal ideation does not mean that someone will act on those thoughts. However, it should never be dismissed or ignored.
When it comes to assessing suicidal ideation, it’s important to approach the situation with the utmost care and sensitivity. Here are some steps and considerations to help assess suicidal ideation:
- Active Listening: Create a safe and non-judgmental space for the individual to express their thoughts and emotions openly. Listen attentively and empathetically, allowing them to share their experiences.
- Ask Direct Questions: While it may feel uncomfortable, asking direct questions about suicidal thoughts can provide valuable insights. Ask gently and without judgment, allowing the person to share their feelings honestly. For example, you can ask, “Are you currently having thoughts of harming yourself?” or “Have you thought about suicide as a way to end your pain?”
- Examine the Intensity and Frequency: Understand the intensity and frequency of their thoughts. Inquire about how often they occur, how long they last, and whether the intensity has increased over time. This information can help gauge the severity of the situation.
- Identify Risk Factors and Warning Signs: Discuss any risk factors that may contribute to their suicidal ideation. These might include a history of mental health issues, previous suicide attempts, substance abuse, or a recent traumatic experience. Additionally, look for warning signs such as withdrawal from loved ones, giving away possessions, or expressing feelings of hopelessness.
- Professional Assessment: Encourage the individual to seek help from a mental health professional who can thoroughly assess the situation. Mental health professionals are trained to ask appropriate questions, evaluate risk, and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
As great as it is for you to help your friend, you’ll want to get the professionals involved, as they can provide the necessary support and guidance throughout the assessment process.
Immediate professional intervention should be sought if there is an immediate risk of harm or if your friend has a clear plan and intent to die by suicide.
Treatments for Suicidal Ideation
Psychotherapy and Counseling
First, encourage them to seek professional help like psychotherapy or counseling. It can make a world of difference. In these therapy sessions, a trained mental health professional will be there for your friend, providing a caring and non-judgmental space to talk about their emotions and thoughts. They offer guidance and help them process what they’re going through.
One effective therapy for suicidal thoughts is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). It helps them identify negative thoughts and behaviors and replace them with more positive and realistic ones. Encourage them to try it, as it can teach them coping skills and reduce their urges to harm themselves.
Another helpful therapy approach is dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). This focuses on teaching your friend how to manage their emotions, handle stress in healthier ways, and communicate effectively. They may attend group therapy sessions and work on building a support network.
Encourage your friend to create a safety plan with their therapist. It’s about identifying people they trust, like family or friends, who can provide support during tough times. Knowing who they can reach out to when they feel overwhelmed can be incredibly comforting. They can also work on strategies to reduce risks, such as limiting access to harmful means.
Remember, you can support your friend by simply being there for them. Listen to them attentively, and let them express their emotions without judgment. Offer a shoulder to lean on and be a source of comfort. Help them find resources, such as helplines or support groups, to offer additional guidance and understanding.
Remind them that it’s okay to ask for help and that seeking assistance is a courageous step. Encourage them to take things one day at a time and reassure them that there are people who care about their well-being.
Medications
In addition to psychotherapy, medication can play a significant role in treating suicidal thoughts. It’s important to note that a qualified healthcare professional, like a psychiatrist or primary care doctor, will carefully evaluate your friend’s situation and determine the best course of action. Medication is not a one-size-fits-all approach, so personalized care is essential.
Antidepressant medications are commonly used to help manage suicidal ideation. They work by balancing certain chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin, which can influence mood and emotions.
By stabilizing these chemicals, these medications can help reduce feelings of hopelessness and despair. However, it’s crucial to remember that medication takes time to take effect, and finding the right one may require some trial and error.
Your friend needs regular follow-ups with their healthcare provider to monitor their progress and make any necessary adjustments to their medication. Patience is key during this process, as it can take several weeks or even months to find the right medication and dosage that works best for them.
Encourage your friend to communicate openly with their healthcare provider about any concerns or side effects they may be experiencing. Adjusting the dosage or trying a different medication can help alleviate these issues. Regular communication ensures the treatment plan is tailored to your friend’s needs.
While medications can be highly effective, they work best when combined with other forms of treatment, such as therapy. Encourage your friend to continue attending therapy sessions and maintain an open line of communication with their therapist. Therapy and medication can provide a comprehensive approach to addressing suicidal thoughts and promoting overall mental well-being.

Alternative and Complementary Treatments
We’re glad you’re interested in learning about alternative and complementary therapies that can provide additional support for someone dealing with suicidal ideation. Let’s explore some of these options together!
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like mindfulness and meditation can help your friend cultivate a sense of calm, reduce stress, and develop a greater awareness of their thoughts and emotions. Encourage them to try meditation apps or guided meditation videos to get started. These techniques can enhance overall well-being and provide a sense of grounding during difficult moments.
- Yoga: Yoga combines physical movement, breathwork, and mindfulness, providing both physical and mental benefits. It can help your friend release tension, improve flexibility, and promote relaxation. Many yoga classes also incorporate mindfulness practices, creating a holistic approach to well-being.
- Exercise: Regular physical exercise has been shown to impact mental health positively. Encourage your friend to engage in activities they enjoy, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or dancing. Exercise helps release endorphins, our brain’s feel-good chemicals, and can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Art Therapy: Engaging in creative activities, such as painting, drawing, or writing, can be a healing outlet for emotions. Art therapy can offer a non-verbal way to express feelings, process emotions, and find a sense of self-expression. Suggest your friend explore art therapy resources or start a journal to document their thoughts and emotions.
- Support Groups: Encourage your friend to join support groups specifically focused on mental health and suicide prevention. Being in a supportive community with others who understand their experiences can provide validation, empathy, and a sense of belonging. Support groups can be in-person or online, offering a safe space to share and learn from others who have gone through similar struggles.
- TMS Therapy: Transcranial magnetic stimulation is a complementary treatment that can help with suicidal thoughts. There’s so much to it that we’re dedicating an entire section to it.
How TMS Therapy Can Help
Transcranial magnetic stimulation, or TMS therapy, is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Research studies have shown that TMS therapy can reduce suicidal thoughts in individuals.
There was even a study that compared individuals who received TMS therapy to those who didn’t, and it found that the people who received TMS had a significant decrease in their suicidal thoughts. That can be life changing.
The interesting thing about TMS therapy is that it can bring about structural and physiological changes in the brain, particularly in the regions involved in regulating mood.
Targeting these areas can help alleviate the intensity of suicidal ideation. Plus, since TMS is non-invasive, it’s considered a safer alternative to more invasive procedures. That’s definitely a great aspect of this treatment!
TMS therapy involves placing magnetic coils on the scalp, which generate magnetic fields that penetrate the skull and induce small electrical currents in specific regions of the brain. These electrical currents are believed to help normalize the activity of the targeted brain regions and improve symptoms of various mental health and neurological conditions.
During a TMS session, the magnetic coils are placed on the patient’s scalp, typically near the forehead. The coils deliver short bursts of magnetic pulses, which generate small electrical currents that stimulate the underlying brain regions.
The specific parameters of the stimulation, such as the intensity and frequency of the pulses, are determined by the healthcare professional and tailored to the individual’s needs. The TMS provider will work directly with your friend to ensure they have the best possible experience.
Building a Support System
Often, when it comes to suicidal ideation, a combination of treatment options will work best for your friend. Psychotherapy, medication, and meditation help a lot of individuals. Adding in TMS therapy can also make a world of difference.
As we mentioned, building a support system can also help. Having a support system can make a world of difference for your friend. They need emotional support, someone who will listen and offer encouragement. Being there for them, lending a compassionate ear, and letting them know you care can bring comfort and hope.
Practical support is equally important. Help your friend with everyday tasks or assist them in navigating the healthcare system. Supporting them in finding mental health resources, attending therapy sessions, or connecting with the right professionals can be immensely helpful.
One significant benefit of a support system is combating feelings of isolation. Your friend might feel disconnected and lonely, so being part of their support system can help bridge that gap. Encourage social interaction, engage in activities together, and empower them to find purpose and meaning in their life.
Accountability is vital, too. As part of your friend’s support system, gently remind them to take their medication, attend therapy appointments, and seek help when they’re struggling. Having someone who looks out for their well-being can be a powerful motivator in their recovery journey.
Above all, remind your friend that you’re here for them. Let them know that you’re there to provide support, compassion, and understanding. Reassure them that it’s okay to lean on others during tough times, and you’ll be right there by their side.
Importance of Continuing Care
It’s essential that your friend continues seeking help and doesn’t stop their treatment. Recovery is a journey, and staying the course is important, even when things are tough. So, let’s talk about why it’s crucial for your friend to keep going.
Firstly, stopping treatment prematurely can worsen things and put your friend’s mental health at risk. Discontinuing medication or therapy abruptly can lead to negative consequences such as worsening symptoms, increased depression, or worsening mood swings. This, in turn, can lead to a sense of hopelessness, increased risk of self-harm, or suicidal ideation.
Secondly, treatment is a process that takes time to achieve its full effects. Mental health issues don’t disappear overnight; the healing process can be long and challenging. You need to remind your friend they are making progress, even if they don’t see it themselves. Encourage them to focus on small steps, day by day, rather than an overnight miracle cure.
Thirdly, a treatment plan usually targets the symptoms and the underlying causes of their mental health issues. Treatment may involve counseling, medication, or combination therapy, which supports mental wellness differently. Discontinuing treatment can thwart progress and lead to a greater probability of symptoms returning or escalating.
Lastly, keeping up with treatment can motivate them to continue the work on themselves and their mental health.
Your friend may have days when they feel hopeless and like giving up, but continuing treatment can help them stay committed to their recovery journey. Moreover, treatment can help your friend learn the necessary coping skills, behaviors, and thought patterns to help them progress toward a happy and fulfilling life.
TMS Therapy With Brain Health Center
As we discussed, TMS therapy can help with suicide ideation. It’s a powerful tool that complements psychotherapy, medication, and the other tools mentioned in this blog. As you support your friend, be sure to tell them about TMS therapy with Brain Health Center. They’re located in St. George, Utah.
Brain Health Center offers free TMS therapy for people like your friend battling suicidal thoughts. Call Brain Health Center at 435.260.5123, or visit our website for more information. Suicide is real, but you don’t have to fight it alone!


















